Last updated: 18 ม.ค. 2564 | 3080 จำนวนผู้เข้าชม |

งานวิจัยโดย หมอรุจ, อ. เทอดพงศ์ และทีมงาน เกี่ยวกับการดูแลรักษาฝ้าด้วยการใช้เลเซอร์
พบว่าได้ผลในระดับหนึ่ง โดยต้องปกป้องแสงแดดด้วยครับ
***ที่สำคัญคือต้องใช้อย่างระมัดระวังโดยเฉพาะในผู้ที่มีสีผิวเข้มครับ***
Laser in treatment of melasma in patients with dark skin types should be careful
Post-inflammatory and rebound hyperpigmentation as a complication after treatment efficacy of telangiectatic melasma with 585 nanometers Q-switched Nd: YAG laser and 4% hydroquinone cream in Skin Phototype III-V
Affiliations expand
PMID: 33002283
DOI: 10.1111/jocd.13756
Fulltext >> https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jocd.13756
Authors
Suparuj Lueangarun 1 Suparuj Ruj Lueangarun Chutimon Namboonlue
1, Therdpong Tempark 2
1Division of Dermatology, Chulabhorn International College of Medicine, Thammasat University, Amphur Klongluang, Pathumthani, Thailand, 12120.
2Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Chulalongkorn University, Pathumwan, Thailand.
Summary
Background:
The potential efficacy of vascular component‐targeted laser has been evaluated for treatment of melasma, which commonly found with the co‐existence of telangiectasia.
Objective:
To evaluate the treatment efficacy and safety of 585‐nm QSNYL and 4% HQ cream combination versus 4% HQ cream alone for telangiectatic melasma in the skin phototype III‐V.
Methods:
Twenty‐one Thai female patients with telangiectatic melasma and Fitzpatrick skin phototype (FPT) III‐V were randomly treated with the 585‐nm QSNYL on one side of the face for five sessions at 2‐week intervals. All patients were assigned to apply HQ cream daily at night on both sides of the face for ten weeks and a broad‐spectrum sunscreen regularly throughout the study. The treatment efficacy and safety were evaluated using the Modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI), biometric evaluation, patient assessment, and adverse effects.
Results:
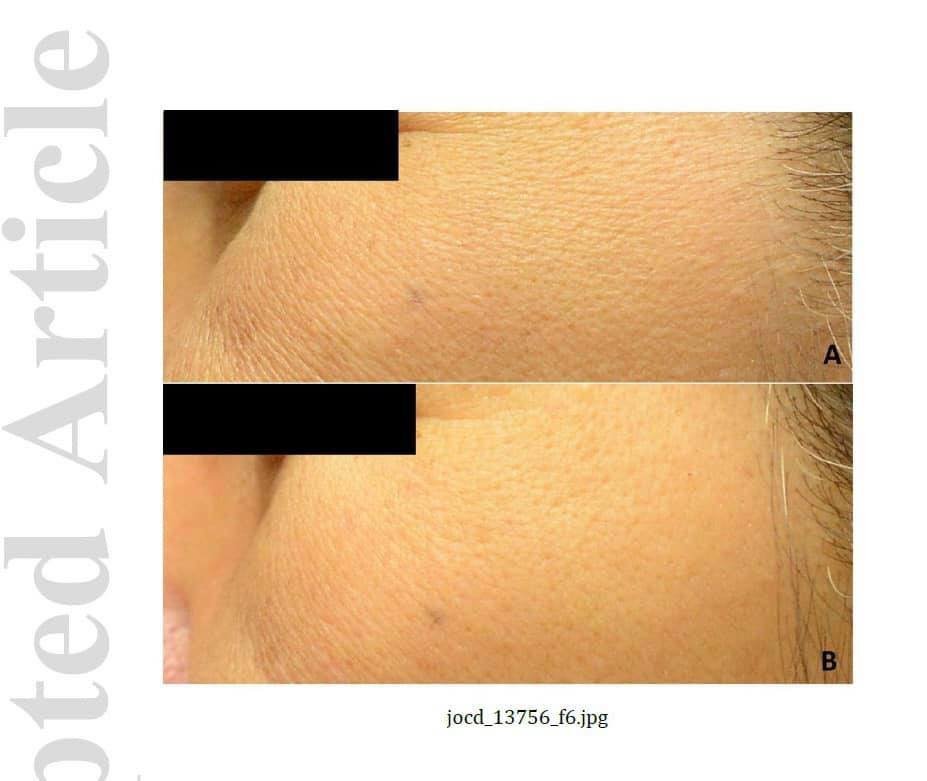
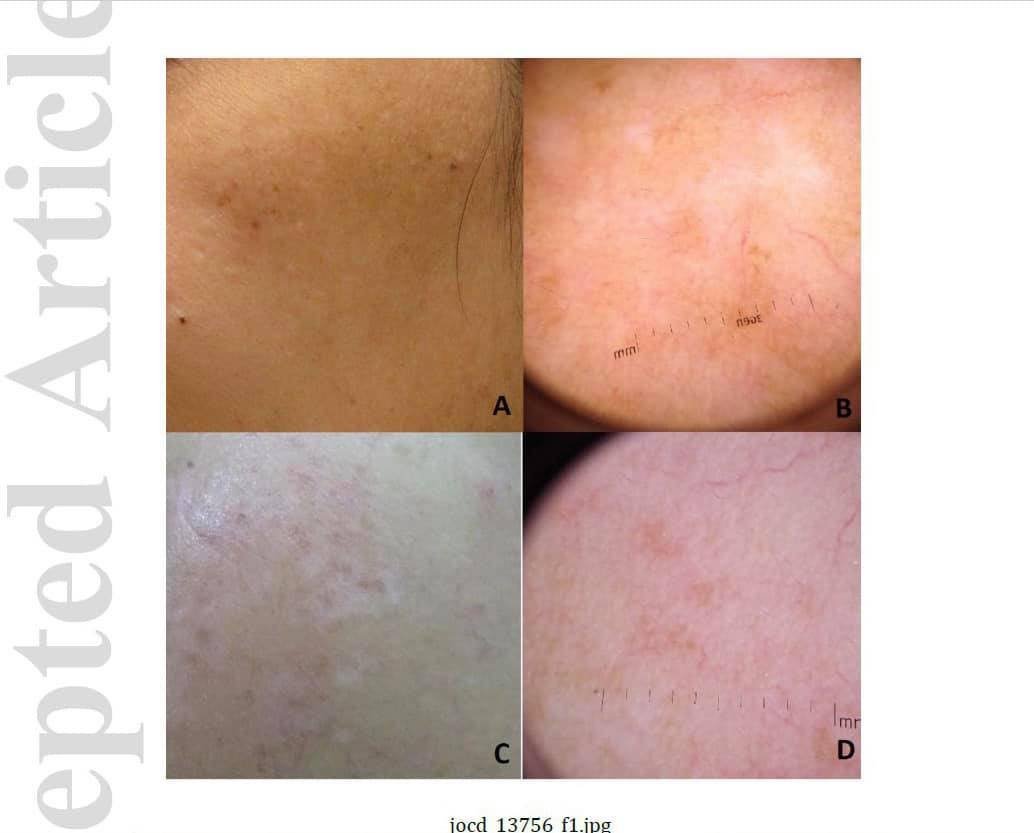
The combination treated side yielded more significant improvement of mMASI than the topical treated side at week 2, 4, and 8, respectively. However, 19% of the patients developed post‐inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) on the laser treated side, especially in FPT IV‐V and rebound hyperpigmentation. There was a significant improvement of hemoglobin and melanin index, but without statistical difference between the two treatment groups.
Conclusions:
The combination of 585‐nm QSNYL and HQ treatment yields treatment efficacy and skin rejuvenation effects for telangiectatic melasma. Nonetheless, a high incidence of PIH and rebound hyperpigmentation is adversely developed in dark FPT. Thus, this laser treatment should be cautiously applied in those with dark FPT IV‐V to avoid laser‐induced pigment alteration..
Keywords: 585 nm Q-Switched Nd: YAG laser; laser therapy; postinflammatory hyperpigmentation; telangiectasia melasma.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33002283/
หมอรุจชวนคุย
.....
References
REFERENCES
1. Sheth VM, Pandya AG. Melasma: a comprehensive update: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65:689-697.
2. Grimes PE. Melasma. Etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131:1453-1457.
3. Kang WH, Yoon KH, Lee ES, et al. Melasma: histopathological characteristics in 56 Korean patients. Br J Dermatol. 2002;146:228-237.
4. Kim EH, Kim YC, Lee ES, Kang HY. The vascular characteristics of melasma. J Dermatol Sci. 2007;46:111-116.
5. Kang HY, Bahadoran P, Suzuki I, et al. In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy detects pigmentary changes in melasma at a cellular level resolution. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19:e228-e233.